Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 5 Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Acids : Acids are sour in taste, turn blue litmus to red, E.g., vinegar, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid.
- Bases: Bases are bitter in taste, feels sopay to touch, turn red litmus to blue e.g. sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, etc.
- Acids produce H+ ions when dissolved in water. H ions cannot exist alone, They combine with water molecule (H2o) to form H3o+ (hydronium ions). It conducts electricity.
- Bases produce OH’ ions when dissolved in water. Bases soluble in water are called It conducts electricity.
- Decrease in HsO or H’ ions concentration per unit volume results in formation of dilute acids or bases respectively.
- It is a highly exothermic reaction.
Acids when dissolved in water release large amount of heat. If water is added to concentrated acid then the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause bums. Hence to avoid bums acid must be added drop wise into water with constant stirring. So that the heat generated spreads over in water.
strong acids → release more H ions → HC1
weak acids →release less number of H+ ions → CH3COOH
strong bases → give more OH” ions → NaOH
weak bases → give less OH’ ions → NH4OH
![]()

Arrhenius Theory:
As per this theory, a substance which gives hydrogen ion (H+) in aqueous solution is called acid. On the other hand, a substance which gives hydroxide ion (OH-) in aqueous solution is called base.
Bronsted Lowry Concept of Acid and Base:
As per this concept, acids are proton donor while bases are proton acceptor.
![]()
Lewis Concept of Acid and Base:
Acids are substances which accept electron pair, while bases are substances which donate electron pair

Reaction of acids and bases with Metals

This reaction is possible only with reactive metals like sodium and potassium.
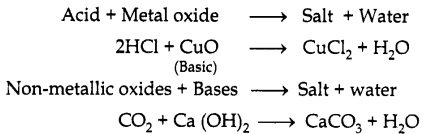
Reaction of acids and bases with Metallic and non-metallic oxides respectively
pH scale:
It is a scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. It is just a number which indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution. The scale ranges from 0 to 14.

Importance of pH in everyday life
- Our body works within pH range of 7.0 to 7.8.
- Acid rain, (pH – 5.6) affects aquatic animals.
- Plants need specific range of pH of soil.
- Acids produced by stomach helps in digestion. If too much acid is formed, people take antacids e.g., milk of magnesia.
- Tooth decay starts when pH in mouth is lower than 5.5. Bacteria present in mouth produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth. Rinsing mouth after eating and using toothpastes which are basic are usually practised for prevention of tooth decay.
- Bee-stings produce acids which causes pain and irritation. Use of baking soda on the sting area gives relief. Stinging hair of nettle leaves inject methanoic acid causing burning pain.
Sodium Chloride:
(NaCl) is also known as common salt. Its pH is 7 because it is made after neutralization between a strong acid and a strong base.
- It is a white powder and having melting point of 1081K.
- It is highly soluble in water and becomes ionized in aqueous solution.
Uses of NaCl
- Sodium chloride is used as common salt in food.
- It is used for preservation of food
- Used in freezing mixture.
- Used as raw material for making sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, bleaching powder, etc.
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH):
It is prepared by chlor-alkali process in which aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine) is electrolysed, products are chlorine and alkaline NaOH.

NaOH is white slippery solid with melting point of 591K. It ionizes in water and thus, conducts electricity.
It is used in paper, silk and petroleum industry, as laboratory reagent etc.
Bleaching Powder:
(CaOCl2) — Calcium oxychloride is prepared by action of chlorine on dry slaked lime Ca(OH)2.
![]()
It is uses as bleaching agent, oxidising agent and disinfectant due to its following property:

Baking soda (NaHCO3) – Sodium hydrogen carbonate is prepared as follows:
![]()
It is a mild non-corrosive basic salt. When it is heated during cooking following reaction takes place:
![]()
It is used as an antacid, soda-acid fire extinguisher and for making baking powder (mixture of baking soda + mild tartaric acid).
When baking power is heated or mixed with water Co2 gas produced in the reaction makes the cake fluffy, soft and spongy.
NaHCo3 + H+ (from acid) → Co2 + H2o + sodium salt of acid
Washing Soda (Na2CO3.10H2O)
Sodium carbonate is prepared on heating baking soda. It is crystallized on adding water.

It is used in making glass, soap and paper, in manufacture of borax, as cleansing agent, to remove permanent hardness of water.
Water of crystallisation:
It is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt. For example,
Na2CO3-10H2O → Washing soda (10H2O is water of crystallisation)
Plaster of Paris (CaSo4– 1/2 H2o)
Calcium sulphate hemihydrate is prepared on heating gypsum at fixed temperature.

Explanation:
One molecule of CaSO4 is attached to 1/2 water molecule, hence 2 units of CaSO4 shares one water molecule [2CaSO4 H2O]
It is used in plastering of fractured bone, in making toys, decoration materials and rough surfaces smooth. Uses of P.O.P. is based on the fact that on mixing with water it changes to gypsum and sets into hard solid mass.
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids.
Saponification:
Fatty acid is heated with aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide to obtain soap. This reaction is called saponification.

Soap is able to show its cleansing property only in soft water.
Calcium and magnesium ions, in hard water, displace sodium from soap molecule and make insoluble precipitate. Hence, soap does not work in hard water.
Detergent:
These are sodium alkyl sulphate or sodium alkyl benzene sulphate. Detergent shows cleansing action in hard water as well.
Calcium and magnesium ions from hard water displace sodium and make sulphonates which are soluble in water. Hence, detergent is able to work in hard water.

A molecule of soap has a hydrocarbon end and a polar end. The hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic and lipophilic. The polar end is hydrophilic and lipophobic. The molecules group together to form a spherical structure called micelle. In a micelle, polar ends are at the surface of sphere while non-polar ends are towards the centre.
The grease is trapped by non-polar ends. Micelle is negatively charged and hence does not make precipitate. This facilitates cleaning of cloths
Leave a Reply